Sugar cane farming is a vital aspect of agricultural practices globally, providing the sweet nectar that fuels industries producing sugar, ethanol, and bioenergy. This article aims to guide passionate sugar cane farmers on the best fertilizer practices to maximize crop yield and minimize costs.
Through this blog, Arihant Group of Industries aims to cover all aspects of sugar cane farming, from planting to harvesting, and everything in between. We will discuss the best cultivation techniques, pest and disease management strategies, and innovative technologies that can revolutionize the sugar cane industry. These strategies have helped many farmers grow their crops.
It highlights the importance of efficient use of fertilizers in achieving healthy and bountiful crops, despite facing numerous challenges in this area. Let us embark on this exciting journey together, empowering ourselves with knowledge and innovation to make a positive impact on the sugar cane industry.
Let’s dive right in!
Here are some common types of sugar:
|
|
These are just a few examples of sugar cane varieties with abbreviated names that are commonly used in agriculture. Each of these varieties may have specific characteristics, such as yield potential, disease resistance, or adaptability to different growing conditions.
When considering types of sugar cane for farming, it’s essential to look for varieties that are well-suited to your specific growing conditions, such as climate, soil type, and pest and disease pressure. Here are some common types of sugar cane varieties used for farming
When choosing sugar cane varieties for farming, it’s essential to consider factors such as yield potential, disease resistance, adaptability to local conditions, and market demand for specific sugar cane products. Consulting with agricultural extension services, local experts, and other growers in your region can provide valuable insights into the most suitable varieties for your farming operation.
Flat planting and furrow planting are two common methods for planting sugar cane. Each method has its advantages and may be preferred based on factors such as soil type, drainage, and equipment availability.

Maximizing sugar cane farming requires a combination of strategic planning, efficient practices, and continuous improvement. Here are some strategies to optimize sugar cane farming:
Choose high-yielding and disease-resistant sugar cane varieties suitable for your region’s climate, soil type, and other environmental conditions. Consult with agricultural experts or local agricultural extension services for recommendations.
Ensure proper soil preparation by conducting soil tests to determine nutrient levels and pH. Implement soil amendments as necessary to optimize soil fertility and structure. Employ techniques such as minimum tillage to reduce soil erosion and maintain soil health.
Plant sugar cane during the appropriate planting season, considering local climate patterns and rainfall. Use healthy and disease-free seed cane, and plant it at the recommended spacing and depth for optimal growth and yield.
Develop a fertilization plan based on soil test results and crop nutrient requirements. Apply fertilizers at the right time and in the correct amounts to ensure adequate nutrient supply throughout the growing season. Consider using organic fertilizers and soil amendments to improve soil health and fertility in the long term.
Timing plays a vital role in maximizing the effects of fertilizer applications. Sugar cane plants have specific growth stages, and fertilizers should be applied accordingly.
During the early growth stages, focus on providing nitrogen-rich fertilizers to promote vigorous leaf and shoot growth. Later in the growth cycle, switch to a fertilizer blend with a higher phosphorus content to support root development and flowering.
To minimize nutrient leaching and ensure efficient uptake, it is essential to adopt appropriate fertilizer application techniques. Split application, where fertilizers are applied in multiple doses during the growing season, can reduce losses and maintain a consistent supply of nutrients to the plants
Implement effective weed control strategies to minimize competition for nutrients, water, and sunlight. Use a combination of cultural practices (such as crop rotation and cover cropping), mechanical methods (such as hand-weeding and cultivation), and judicious use of herbicides to manage weeds efficiently.
Monitor sugar cane fields regularly for signs of pest infestations and diseases. Implement integrated pest management (IPM) strategies, including biological control, cultural practices, and targeted use of pesticides, to minimize pest damage and reduce reliance on chemical inputs.
Manage irrigation efficiently to ensure adequate moisture levels for sugar cane growth, especially during critical growth stages. Use irrigation scheduling techniques based on crop water requirements, soil moisture monitoring, and weather forecasts to optimize water use efficiency and minimize water stress.
Time harvesting operations to coincide with optimal sugar content and maturity levels. Use appropriate harvesting equipment and techniques to minimize losses and damage to the cane stalks. Implement proper post-harvest handling practices to preserve sugar quality during transportation and processing.
Practice crop rotation with legumes or other non-sugar cane crops to improve soil fertility, break pest and disease cycles, and reduce soil erosion. Diversify farm income by integrating other compatible crops or livestock into sugar cane farming systems.
Monitor key performance indicators such as yield, sugar content, input costs, and profitability regularly. Keep abreast of new research, technological advancements, and best practices in sugar cane farming, and be willing to adapt your strategies accordingly to optimize farm productivity and sustainability.
By implementing these strategies and continuously improving farming practices, sugar cane growers can maximize yields, quality, and profitability while promoting environmental sustainability and resilience in their farming operations.
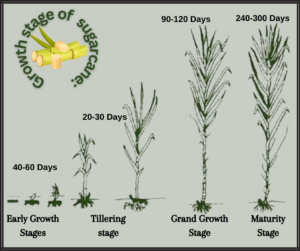
Stage-wise application of fertilizer for sugarcane farming is an important aspect of maximizing crop productivity. Here is a general guideline for fertilizer application during different stages of sugarcane growth:
Note: The above recommendations may vary based on soil type, nutrient levels, climate, and specific regional requirements. It is advisable to consult local agricultural experts or agricultural extension services for precise fertilizer recommendations tailored to your sugarcane farming conditions.
Sugarcane typically takes around 9 to 24 months to grow, depending on various factors such as climate, variety, soil conditions, and agricultural practices. In tropical regions with favorable conditions, sugarcane can mature in about 9 to 12 months.
However, in less favorable environments or with specific varieties, it can take up to 18 to 24 months to reach maturity. It’s important to note that sugarcane is a perennial crop, meaning it can be harvested multiple times from the same plant before replanting is necessary.
Fertilizers significantly enhance crop yield and quality in sugar cane farming, offering numerous benefits, including improved growth and productivity.
Fertilizers provide essential nutrients in concentrated form, enhancing the growth and development of sugar cane plants.
Fertilizers contain nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, which are essential for the growth and development of sugar cane plants.
Fertilizers increase the size and weight of sugar cane stalks, resulting in higher yields.
Fertilizers provide the right balance of nutrients required for sucrose synthesis, enhancing the quality of sugar cane.
Fertilizers ensure a balanced ratio of nutrients for optimal growth, preventing nutritional deficiencies or excesses.
Fertilizers indirectly contribute to weed suppression by promoting the rapid growth and development of sugar cane plants, reducing the need for manual or chemical weed control methods.
Fertilizers contribute to environmental sustainability in sugar cane farming by maximizing crop production on limited land and optimizing nutrient use efficiency.
Initial considerations as to choosing mature stalks with a strong texture and rich color for sugarcane harvesting. Cut the stalks close to the ground using a machete or other specialized harvesting instrument, allowing about 6 inches of plant for regrowth. Clear the gathered stalks of any leaves and dirt. After that, package the stalks and deliver them to a facility for processing.
The juice from the crushed sugarcane is processed into sugar or other goods at the factory. For the sugarcane crop to be harvested successfully and to give its greatest yield and quality, appropriate time and technique are essential.
In conclusion, to maximize sugar cane cultivation, meticulous planning, effective methods, and ongoing adaptability are needed. Farmers may maximize their productivity, quality, and profitability by choosing the best sugar cane types, using the best planting techniques, and adhering to strategic procedures for fertilization, weed and insect control, irrigation management, and crop rotation.
Sugar cane growing will be successful and sustainable if regular monitoring, new technology, and best practices are used, and industry advancements and research are kept up to date. Sugar cane producers can ensure environmental sustainability and resilience in their agricultural operations, while also having a beneficial influence on the industry, by using these measures and continuously improving their practices.
So let’s adopt these tactics, transform the sugar cane sector, and keep savoring the sweetness.
Do you want to know more? let us know your thoughts on DMs

